Table of Contents
The PFAS Compliance Challenge
Compliance engineers confront increasingly complex PFAS regulations spanning federal, state, and international levels. Gaps in supplier data, varied reporting formats, and fast-changing waste disposal laws can quickly derail compliance efforts.
What’s New in PFAS Regulations (Updated 2025)
-
TSCA Section 8(a)(7) requires all U.S. electronics manufacturers and importers to report intentionally added PFAS by May 1, 2025—including PFNA, PFHxS, and related PFAS.
-
Maine’s PFAS Ban mandates elimination of intentionally added PFAS in all products by January 1, 2030, unless exempt as “currently unavoidable.”
-
Canada’s PFAS CEPA Section 71, effective by March 24, 2025, forces PFAS reporting, covering over 300 listed PFAS compounds.
-
EU REACH PFAS Restriction applies to PFOA, PFNA, PFHxS, and PFOS (≤25 ppb) under Annex XVII, with total PFAS bans emerging.
Common PFAS Docs to Collect
-
Material Declarations (FMD templates)
-
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
-
Supplier PFAS Test Reports (targeted: LC–MS/MS)
-
PFAS-specific certifications (TSCA, REACH, CEPA)
Key PFAS Compliance Gaps Engineers See
-
Regulatory Diversity: Disparate US, EU, CA, and ME PFAS rules
-
Supplier Transparency: Slow or incomplete declarations
-
Data Integrity: Conflicting or outdated test reports
-
Waste Handling: PFAS landfill leaching and disposal limits
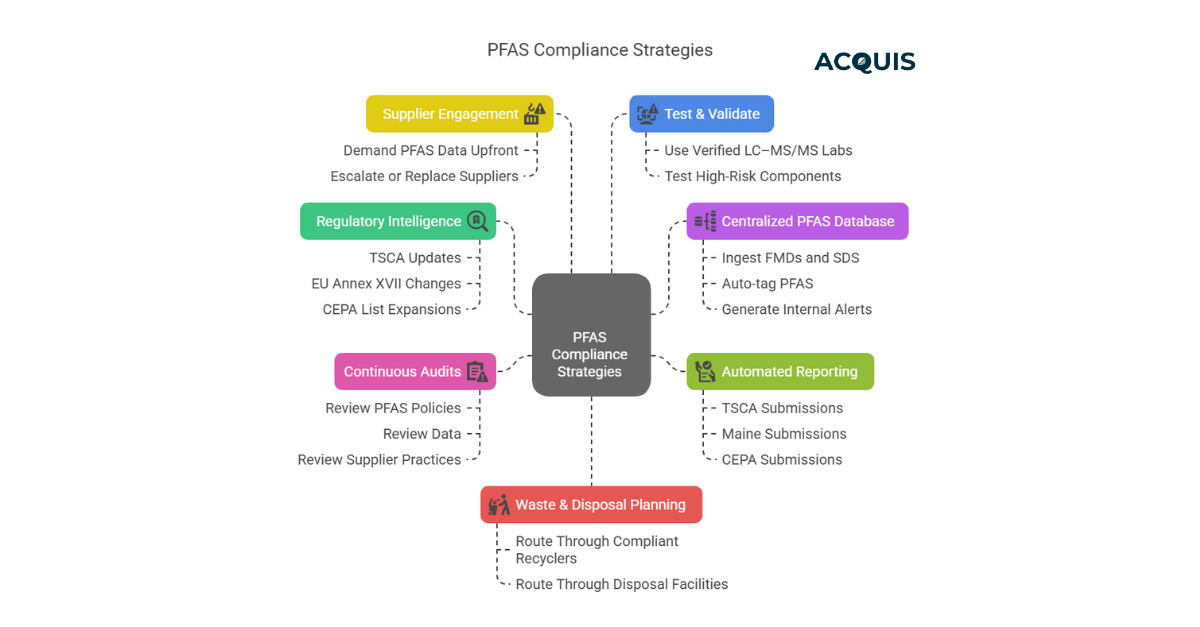
PFAS Compliance Strategies That Work
-
Regulatory Intelligence – Auto-monitor TSCA PFAS list updates, EU Annex XVII changes, and CEPA list expansions.
-
Centralized PFAS Database – Ingest FMDs and SDS, auto-tag PFNA, PFOS, PTFE, PFCAs, and generate internal alerts.
-
Supplier Engagement – Demand PFAS data upfront; escalate or replace suppliers who stall.
-
Test & Validate – Use verified LC–MS/MS labs to test high-risk components.
-
Waste & Disposal Planning – Ensure PFAS-containing waste is routed through compliant recyclers or disposal facilities.
-
Automated Reporting – Generate PFAS data submissions for TSCA, Maine, CEPA with audit trails.
-
Continuous Audits– Regular reviews of PFAS policies, data, and supplier practices.
Tools That Make a Difference
-
Regulation dashboards for TSCA, CEPA, Maine
-
Supplier collaboration platforms for FMD and PFAS data exchange
-
PFAS inventory & labeling modules in EHS/PLM systems
Conclusion
Compliance engineers are at the forefront of managing PFAS compliance in an environment of ever-evolving regulations. To excel in this role, it's essential to stay informed, adopt efficient compliance strategies, and leverage innovative tools. With the right knowledge and resources, compliance engineers can navigate the complex world of PFAS regulations effectively, ensuring that products meet the highest compliance standards. Empower yourself with the right tools and strategies to conquer the PFAS compliance challenge.
